Multi-Objective Optimization of Energy-Efficient Base Station Placement for Hybrid Highway Networks Supporting Autonomous Vehicle Mobility
Corresponding email: hasanahputri@telkomuniversity.ac.id
Published at : 01 Dec 2025
Volume : IJtech
Vol 16, No 6 (2025)
DOI : https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v16i6.7833
| Hasanah Putri | School of Electrical Engineering, Telkom University, Bandung 40257, Indonesia |
| Rendy Munadi | School of Electrical Engineering, Telkom University, Bandung 40257, Indonesia |
| Sofia Naning Hertiana | School of Electrical Engineering, Telkom University, Bandung 40257, Indonesia |
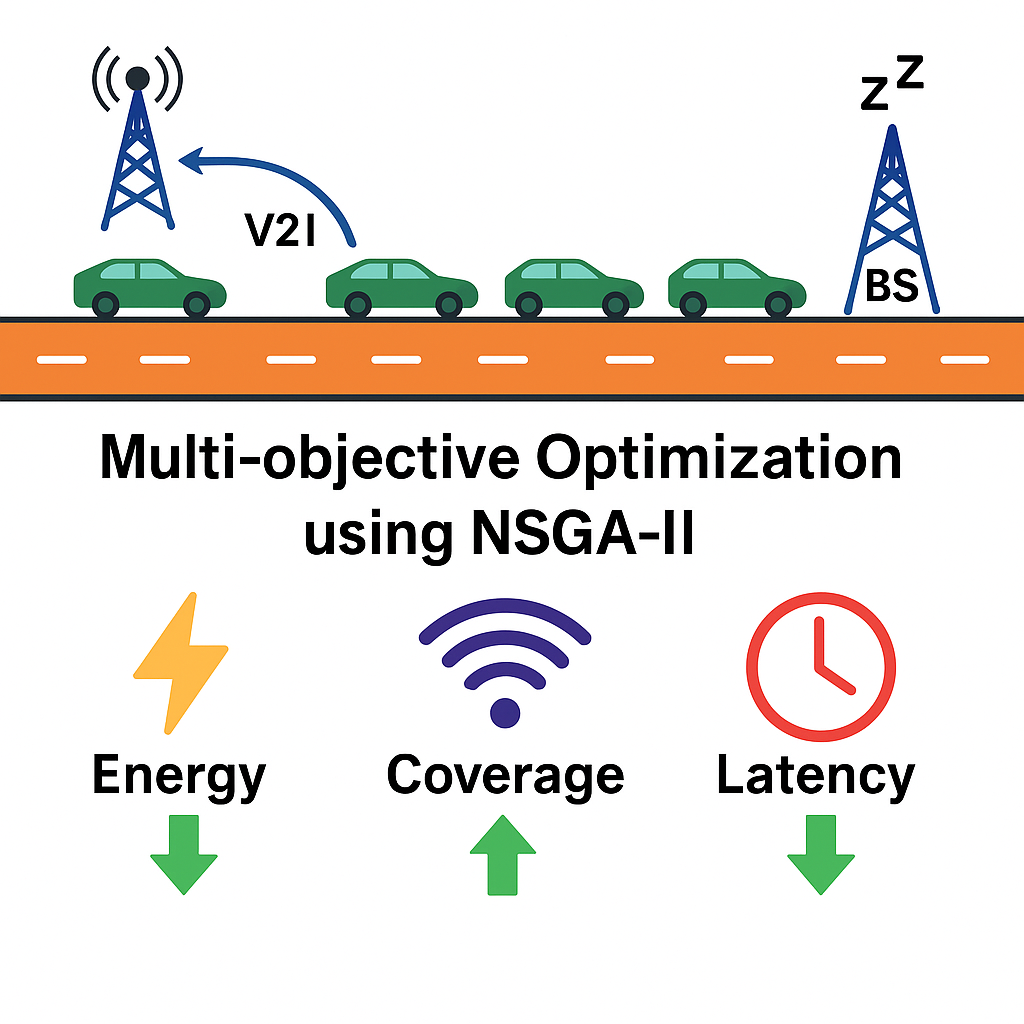
Theincreasing deployment of Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) on highways presents new challenges for the underlying communication infrastructure, which must ensure low latency, high reliability, and energy efficiency. This study proposes a novel approach for Base Satation (BS) placement in the hybrid fiber-wireless networks specifically designed for linear highway environments. By formulating the deployment as a multi-objective op timization problem, the model simultaneously minimizes total network energy consump tion and end-to-end latency while maximizing highway coverage. A dynamic traffic-aware sleep mode mechanism is also introduced to reduce power usage during low-density traffic conditions. The Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm II (NSGA-II) is employed to explore Pareto-optimal configurations, and the simulation results demonstrate signifi cant trade-offs among the objectives. The proposed framework reduces the Base Satation (BS) energy consumption by up to 40% while maintaining a latency below 10 ms and achieving coverage above 95%. These findings offer an effective deployment strategy for next-generation vehicular communication networks.
5G and beyond; Autonomous vehicles; Energy efficiency; Hybrid network architecture; Multi-objective optimization
