Structure, Density and Hardness of Spark Plasma Sintered Fe-Mn Alloys
Corresponding email: toto009@brin.go.id
Published at : 01 Dec 2025
Volume : IJtech
Vol 16, No 6 (2025)
DOI : https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v16i6.7789
| Sovian Aritonang | Faculty of Military Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Indonesia Defense University, Bogor 16810, Indonesia |
| Andy Marjono Putranto | 1. Faculty of Military Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Indonesia Defense University, Bogor 16810, Indonesia; 2. Organization and Human Resources Bureau, National Research and Innovation Agency, Jak |
| Resetiana Dwi Desiati | Research Center for Advanced Material, National Research and Innovation Agency, Tangerang Selatan 15314, Indonesia |
| Bambang Hermanto | Research Center for Advanced Material, National Research and Innovation Agency, Tangerang Selatan 15314, Indonesia |
| Michael Tulus Samuel | Faculty of Military Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Indonesia Defense University, Bogor 16810, Indonesia |
| Andi Suhandi | Research Center for Advanced Material, National Research and Innovation Agency, Tangerang Selatan 15314, Indonesia; |
| Oman Zuas | Research Center for Testing Technology and Standards, National Research and Innovation Agency, Tangerang Selatan 15314, Indonesia |
| Tony Wang | Central Analytical Research Facility (CARF), Queensland University of Technology (QUT), Brisbane, QLD 4000, Australia |
| Maykel T.E. Manawan | 1. Faculty of Military Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Indonesia Defense University, Bogor 16810, Indonesia 2. Research Center for Advanced Material, National Research and Innovation Agency, Tanger |
| Toto Sudiro | Research Center for Advanced Material, National Research and Innovation Agency, Tangerang Selatan 15314, Indonesia |
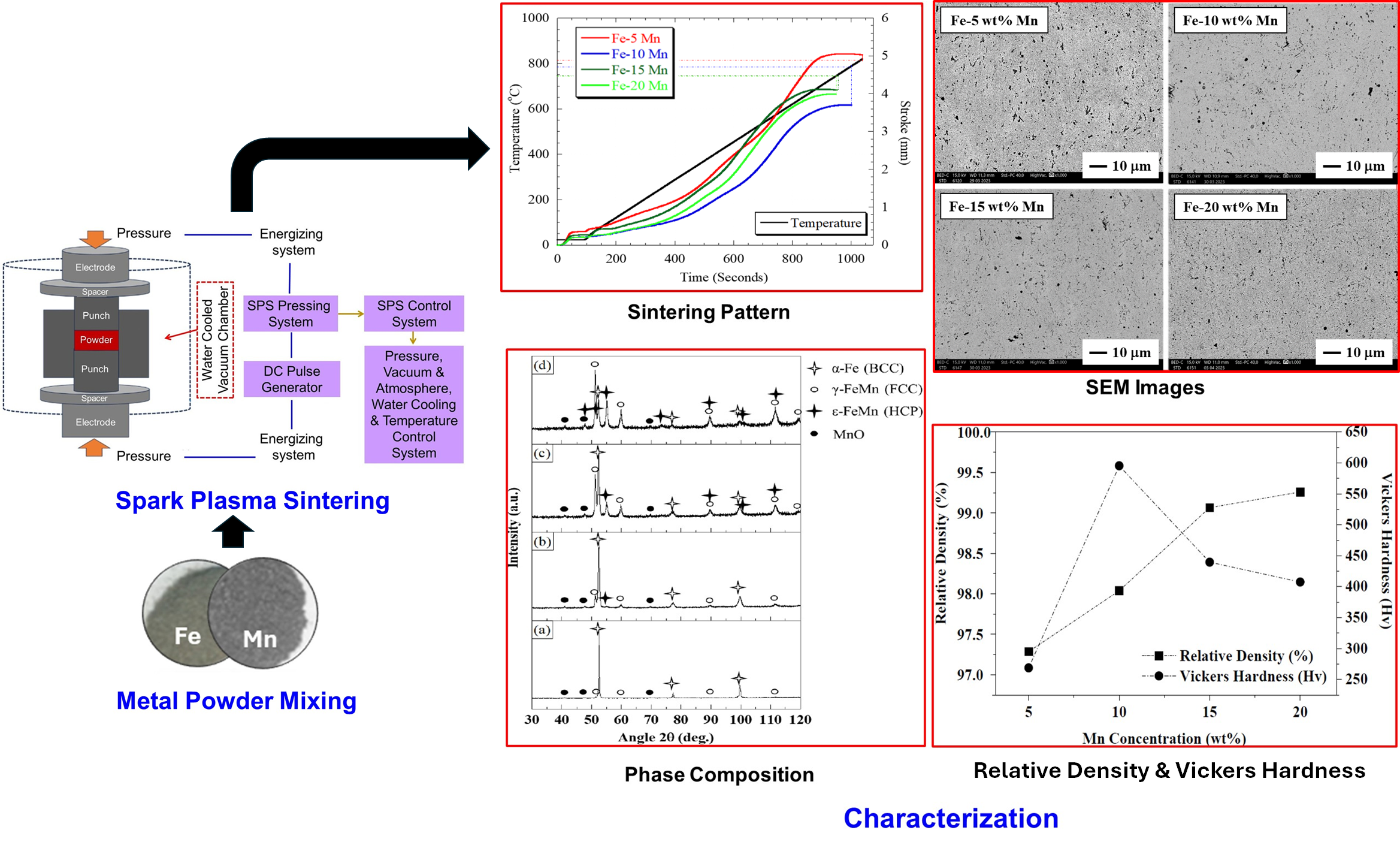
This study examines the effect of Mn content on phase evolution, density, andô its correlation with the hardness of Fe-Mn alloys produced through mechanical millingô followed by a spark plasma sintering technique. Alloys with Mn concentrations of 5,ô 10, 15, and 20 wt% were examined, revealing phase compositions primarily consistingô of BCC (-Fe, ferrite), FCC (
-FeMn, austenite), and HCP (
-FeMn, martensite), withô minor occurrences of MnO. The Mn content significantly affected the phase distribution,ô strain, crystallite size, and relative density. The evolution of phase structureãparticularlyô the balance between hard BCC, HCP, and softer FCCãemerges as a critical factor inô determining hardness. The alloy with 10 wt% Mn exhibited the highest hardness (
595.34ô Hv) despite not having the highest density, indicating that densification and the natureô and proportion of constituent phases governed the mechanical properties. While ferriteô and martensite enhance hardness, increasing the Mn content promotes the formation ofô a more ductile austenite phase, which offsets the strengthening effects and contributesô to the observed decrease in hardness at higher Mn levels. These findings highlight theô complex interplay between phase transformation, microstructure, and hardness in Fe-Mnô alloy systems.
BCC; Density; Fe-Mn; Hardness; Spark plasma sintering
Abdul, A., Yang, M., Shimizu, T., &
Furushima, T. (2021). Effect of grain misorientation and martensitic
transformation on surface roughening behavior in thin austenitic stainless
steel foils. International
Journal of Technology, 12(6), 1161ã1167. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v12i6.5180
Acet, M., Schneider, T., Gehrmann, B., & Wassermann, E. F. (1995). The
magnetic aspects of the ?ã? and ?ã? martensitic transformations in FeãMn
alloys. Journal de Physique IV, 5, C8-379ãC8-384. https://doi.org/10.1051/jp4:1995856
Amaral, R., Santos, A. D., Sousa, J.
A., & Lopes, A. B. (2017). The influence of microstructure on the
mechanical behaviour of dual phase steels. In L. F. M. da Silva (Ed.), Materials
design and applications (pp. 25ã35). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50784-2_3
Anwar, M. S., Melinia, R. K., Pradisti,
M. G., & Siradj, E. S. (2021). Effect of prior austenite grain-size on the
annealing twin density and hardness in the austenitic stainless steel. International
Journal of Technology, 12(6), 1149ã1160. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v12i6.5190
Ayodele, O. O., Awotunde, M. A.,
Babalola, B. J., & Olubambi, P. A. (2021). Spark plasma sintering of
CNTãNiAl nanocompositesãprocess parameter, densification mechanism, and grain
analysis. Manufacturing Review, 8, 25. https://doi.org/10.1051/mfreview/2021023
Balagurov, A. M., Bobrikov, I. A.,
Pons, J., Cifre, J., Sun, L. Y., & Golovin, I. S. (2018). Structure of the
FeãMnãSi alloys submitted to ? ? ? thermocycling. Materials
Characterization, 141, 223ã228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2018.04.052
Balbo, A., & Sciti, D. (2008).
Spark plasma sintering and hot pressing of ZrB?ãMoSi? ultra-high-temperature
ceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 475(1), 108ã112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2007.01.164
Cabibbo, M., Deodati, P., Libardi, S., Molinari, A., Montanari, R., &
Ucciardello, N. (2008). Damping of FeMo alloys obtained from SPS
sintering of nanostructured powders. Materials Science Forum, 604ã605,
203ã211. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.604-605.203
Cheary, R. W., Coelho, A. A., &
Cline, J. P. (2004). Fundamental parameters line profile fitting in laboratory
diffractometers. Journal of Research of the National Institute of Standards
and Technology, 109, 1ã25. https://doi.org/10.6028/jres.109.002
Chen, X., Duan, H., Cao, B., Sun, Q.,
& Yang, W. (2022). The evolution mechanism of an FeMo alloy catalyst for
growth of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Physical Chemistry Chemical
Physics, 24, 25480ã25486. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2CP03182E
Choi, S., Jeon, J., Seo, N., Moon, Y.
H., Shon, I.-J., & Lee, S.-J. (2020). Effect of composition on
strain-induced martensite transformation of FeMnNiC alloys fabricated by powder
metallurgy. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials, 65(3), 1001ã1004. https://doi.org/10.24425/amm.2020.133206
Citrawati, F., Dwiwandono, R., &
Firmansyah, L. (2020). The effect of Ni on the formation of bainite in FeãNi
lateritic steels through semi-continuous cooling method. International
Journal of Technology, 11(1), 60ã70. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v11i1.3178
Danninger, H., Gierl-Mayer, C.,
Prokofyev, M., Huemer, M.-C., De Oro Calderon, R., Hellein, R., Mû¥ller, A.,
& Stetina, G. (2021). Manganeseãa promising element also in high alloy
sintered steels. Powder Metallurgy, 64(2), 115ã125. https://doi.org/10.1080/00325899.2021.1886717
Ding, Z., Ding, C., Yang, Z., Zhang,
H., Wang, F., Li, H., Xu, J., Shan, D., & Guo, B. (2024). Ultra-high
strength in FCC+BCC high-entropy alloy via different gradual morphology. Materials,
17(18). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17184535
Ekholm, M., & Abrikosov, I. A.
(2011). Structural and magnetic ground-state properties of ?-FeMn alloys from
ab initio calculations. Physical Review B, 84, 104423. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.84.104423
Farihin, P., Suharno, B., Dani, M.,
Ngarayana, I. W., Andryansyah, Insani, A., Wardana, R. I., Huang, C. A., Aziz,
F., & Adhika, D. R. (2025). High-resolution neutron diffraction analysis of
residual stresses in oxide dispersion strengthened FeNiCrY?O? cast alloys for
advanced nuclear reactor applications. International Journal of Technology,
16(2), 625ã638. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v16i2.7241
Feng, Y. P., Blanquer, A., Fornell, J.,
Zhang, H., Solsona, P., Barû°, M. D., SuriûÝach, S., IbûÀûÝez, E., GarcûÙa-Lecina,
E., Wei, X., Li, R., Barrios, L., Pellicer, E., Noguûˋs, C., & Sort, J.
(2016). Novel FeãMnãSiãPd alloys: Insights into mechanical, magnetic, corrosion
resistance and biocompatibility performances. Journal of Materials Chemistry
B, 4, 6402ã6412. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TB01951J
Gambaro, S., Paternoster, C.,
Occhionero, B., Fiocchi, J., Biffi, C., Tuissi, A., & Mantovani, D. (2021).
Mechanical and degradation behavior of three FeãMnãC alloys for potential
biomedical applications. Materials Today Communications, 27, 102250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtcomm.2021.102250
Hasegawa, T., Kanatani, S., Kazaana,
M., Takahashi, K., Kumagai, K., Hirao, M., & Ishio, S. (2017). Conversion
of FeCo from soft to hard magnetic material by lattice engineering and
nanopatterning. Scientific Reports, 7, 13215. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-13602-x
Idhil, A., Borca, C., Uldry, A.-C.,
Zema, N., Turchini, S., Catone, D., Foelske, A., Grolimund, D., & Samaras,
M. (2012). The influence of Cr composition on the local magnetic structure of
FeCr alloys. Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Section B,
284, 1ã5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2011.08.071
Kang, L., Yuan, H., Li, H., Ji, Y., Liu, H., & Liu, G. (2021). Enhanced
mechanical properties of FeãMnãAlãC low density steel via aging treatment. Frontiers
in Materials, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmats.2021.680776
Kern, A., Coelho, A. A., & Cheary,
R. W. (2004). Convolution based profile fitting. In E. J. Mittemeijer & P.
Scardi (Eds.), Diffraction analysis of the microstructure of materials
(pp. 17ã50). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-662-06723-9_2
Khan, F., & Rashed, H. M. M. A.
(2020). Phase transformation in micro-alloyed steels. In A. Sharma, Z.
Duriagina, & S. Kumar (Eds.), Engineering steels and high entropy
alloys. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.91468
Kim, H., Suh, D.-W., & Kim, N. J.
(2013). FeãAlãMnãC lightweight structural alloys: A review on the
microstructures and mechanical properties. Science and Technology of
Advanced Materials, 14, 014205. https://doi.org/10.1088/1468-6996/14/1/014205
Kisku, N. (2024). Development of novel
low density ultra-high strength manganese-steel with significant ductility
through thermo-mechanical processing route. Materials Science and
Engineering: A, 901, 146591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2024.146591
Kochma?ski, P., Chyli?ska, R., Figiel,
P., Fryska, S., Kochma?ska, A. E., Kwiatkowska, M., Kwiatkowski, K., Niemczyk,
A., S?owik, J., Maziarz, W., Rogal, L., Dybowski, K., & Baranowska, J.
(2024). Influence of chemical composition on structure and mechanical
properties of vacuum-carburized low-alloy steels. Materials, 17(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17020515
Krauss, G. (2015). Steels:
Processing, structure, and performance (2nd ed.). ASM International. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.tb.spsp2.9781627082655
Krû¥ger, J. T., Hoyer, K.-P., Huang, J.,
Filor, V., Mateus-Vargas, R. H., Oltmanns, H., Meiûner, J., Grundmeier, G.,
& Schaper, M. (2022). FeMn with phases of a degradable Ag alloy for
residue-free and adapted bioresorbability. Journal of Functional
Biomaterials, 13(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13040185
Kuhn, H., & Medlin, D. (2000). Mechanical
testing and evaluation (Vol. 8). ASM International. https://doi.org/10.31399/asm.hb.v08.9781627081764
Le Godec, Y., & Le Floch, S.
(2023). Recent developments of high-pressure spark plasma sintering: An
overview of current applications, challenges and future directions. Materials,
16(3). https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/16/3/997
Lemke, J. N., Fiocchi, J., Biffi, C.
A., Tuissi, A., Copes, F., Paternoster, C., Mantovani, D., & Coda, A.
(2025). Design, development and performance of a FeãMnãSiãCu alloy for
bioabsorbable medical implants. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 13,
2737ã2752. https://doi.org/10.1039/D4TB01635A
Li, C.-M., Sommer, F., &
Mittemeijer, E. J. (2002). Characteristics of the ? ? ? transformation in FeãMn
alloys. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 325(1), 307ã319. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01459-9
Liu, T.-W., & Wu, X.-L. (2024).
Martensitic transformation pathways and crystallographic orientation
relationships in steel. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,
174, 74ã84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmst.2023.06.060
Malamud, F., Guerrero, L., La Roca, P.,
Sade, M., & Baruj, A. (2018). Role of Mn and Cr on structural parameters
and strain energy during FCCãHCP martensitic transformation in FeãMnãCr shape
memory alloys. Materials & Design, 139, 314ã323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2017.11.017
Mani, M. K., Viola, G., Reece, M. J.,
Hall, J. P., & Evans, S. L. (2012). Structural and magnetic
characterization of spark plasma sintered Feã50Co alloys. MRS Online
Proceedings Library, 1516, 201ã207. https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.1669
Milititsky, M., Van Caenegem, N., &
De Cooman, B. C. (2008). Structural and magnetic transformations in the FeãMn
binary system. Steel Research International, 79, 156ã159. https://doi.org/10.1002/srin.200806331
Mola, J., & Ren, M. (2018). On the
hardness of high carbon ferrous martensite. IOP Conference Series: Materials
Science and Engineering, 373, 012004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/373/1/012004
Mukhopadhyay, N. K., Ali, F., Scudino,
S., Samadi Khoshkhoo, M., Stoica, M., Srivastava, V. C., Uhlenwinkel, V.,
Vaughan, G., Suryanarayana, C., & Eckert, J. (2014). Inverse
HallãPetch-like mechanical behaviour in nanophase AlãCuãFe quasicrystals: A new
phenomenon. Acta Physica Polonica A, 126, 543ã548. https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.126.543
Naik, S. N., & Walley, S. M.
(2020). The HallãPetch and inverse HallãPetch relations and the hardness of
nanocrystalline metals. Journal of Materials Science, 55, 2661ã2681. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-019-04160-w
Oh, S.-J., Park, D., Kim, K., Shon,
I.-J., & Lee, S.-J. (2018). Austenite stability and mechanical properties
of nanocrystalline FeãMn alloy fabricated by spark plasma sintering with
variable Mn content. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 725, 382ã388.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.04.051
Oladijo, O., Popoola, A., Ujah, C.,
& Namoshe, M. (2019). Dataset of spark plasma sintering of AlãZnãSn alloy
for soft solder application. Data
in Brief, 24, 103948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2019.103948
Paul, B., Kiel, A., Otto, M., Gemming, T., Hoffmann, V., Giebeler, L.,
Kaltschmidt, B., Hû¥ttten, A., Gebert, A., Kaltschmidt, C., & Hufenbach, J.
(2024). Inherent antibacterial properties of biodegradable FeMnC(Cu)
alloys for implant application. ACS Applied Bio Materials, 7, 839ã852. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.3c00835
Qayoom, M., & Dar, G. N. (2020).
Crystallite size and compressive lattice strain in NiFe?O? nanoparticles as
calculated in terms of various models: Influence of annealing temperature. International
Journal of Self-Propagating High-Temperature Synthesis, 29, 213ã219. https://doi.org/10.3103/S1061386220040111
Sabzi, M., & Farzam, M. (2019).
Hadfield manganese austenitic steel: A review of manufacturing processes and
properties. Materials Research Express, 6, 1065c2. https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab3ee3
Saliba, L., Sammut, K., Tonna, C.,
Pavli, F., Valdramidis, V., Gatt, R., Giordmaina, R., Camilleri, L., Atanasio,
W., Buhagiar, J., & Schembri Wismayer, P. (2023). FeMn and FeMnAg
biodegradable alloys: An in vitro and in vivo investigation. Heliyon,
9(5), e15671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15671
Shongwe, M., Ramakokovhu, M., Diouf,
S., Durowoju, M., Obadele, B., Sule, R., Lethabane, M., & Olubambi, P.
(2016). Effect of starting powder particle size and heating rate on spark
plasma sintering of FeNi alloys. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 678,
241ã248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.270
Siripath, N., Suranuntchai, S., &
Sucharitpwatskul, S. (2024). Modeling dynamic recrystallization kinetics in BS
080M46 medium carbon steel: Experimental verification and finite element
simulation. International Journal of Technology, 15(5), 1292ã1307. https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v15i5.6770
Sun, L., Cheverikin, V., & Golovin,
I. (2019). Mechanical spectroscopy as an in situ tool to study anelasticity of
martensitic transition in Feã16Mnã8Crã2Co alloy. Materials Letters, 256,
126635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126635
Taryana, Y., Wahyu, Y., Manaf, A.,
Manawan, M., & Ariadi, W. (2022). Structural and microwave absorption
properties of BaFe????xSn?Zn?O?? (x = 0.05ã1.0) ceramic magnets. Materialia,
23, 101455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2022.101455
Tokita, M. (2013). Spark plasma
sintering (SPS) method, systems, and applications. In Handbook of advanced
ceramics (pp. 1149ã1177). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-385469-8.00060-5
Wang, Y., Wu, C., Liu, Y., Tian, M.,
Lu, X., & Su, X. (2023). Insight into the FCC?HCP transformation in Co-rich
CoãCrãFeãMnãNi high-entropy alloys. Metals, 13(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/met13030504
Wei, F., Cheng, B., Chew, L. T., Lee,
J. J., Cheong, K. H., Wu, J., Zhu, Q., & Tan, C. C. (2022). Grain
distribution characteristics and effect of diverse size distribution on the
HallãPetch relationship for additively manufactured metal alloys. Journal of
Materials Research and Technology, 20, 4130ã4136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.09.006
Xu, Z., Jin, C., Xia, A., Zhang, J.,
& Zhu, G. (2013). Structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline
nickel-rich FeãNi alloy powders prepared via hydrazine reduction. Journal of
Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 336, 14ã19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.02.007
Yan, X., Li, Q., Yin, S., Chen, Z., Jenkins, R., Chen, C., Wang, J., Ma,
W., Bolot, R., Lupoi, R., Ren, Z., Liao, H., & Liu, M. (2019). Mechanical
and in vitro study of an isotropic Ti6Al4V lattice structure fabricated using
selective laser melting. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 782, 209ã223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.12.220
Yin, F., Cheng, G. J., Xu, R., Zhao,
K., Li, Q., Jian, J., Hu, S., Sun, S., An, L., & Han, Q. (2018).
Ultrastrong nanocrystalline stainless steel and its HallãPetch relationship in
the nanoscale. Scripta Materialia, 155, 26ã31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.06.014
Zhang, X., Zhao, Q., Liu, C., Peng, Y.,
Huang, Y., Kong, J., & Wang, K. (2024). On the formation of oxide
inclusions in the high nitrogen chromiumãmanganese steel produced by wire and
arc additive manufacturing. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,
33, 3852ã3863. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.10.103
Zhang, X., Wang, Q., Kane, J. J., Rufner, J. F., & Sun, C. (2023). Graded microstructure and mechanical properties of spark plasma sintered FeãCr alloys. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 967, 171448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.171448
