Integral Indicator Assessment of Municipalities Sustainability in the Leningrad Region
Corresponding email: tanina_av@spbstu.ru
Published at : 29 Dec 2023
Volume : IJtech
Vol 14, No 8 (2023)
DOI : https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v14i8.6835
Tanina, A., Orel , A., Zaborovskaia, O., Tanin, E., 2023. Integral Indicator Assessment of Municipalities Sustainability in the Leningrad Region. International Journal of Technology. Volume 14(8), pp. 1694-1705
| Anna Tanina | Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Polytechnicheskaya, 29, St. Petersburg, 195251, Russia |
| Alexander Orel | State Institute of Economics, Finance, Law and Technology, Roschinskaya, 5, Gatchina, 188306, Russia |
| Olga Zaborovskaia | State Institute of Economics, Finance, Law and Technology, Roschinskaya, 5, Gatchina, 188306, Russia |
| Evgenii Tanin | Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University, Polytechnicheskaya, 29, St. Petersburg, 195251, Russia |
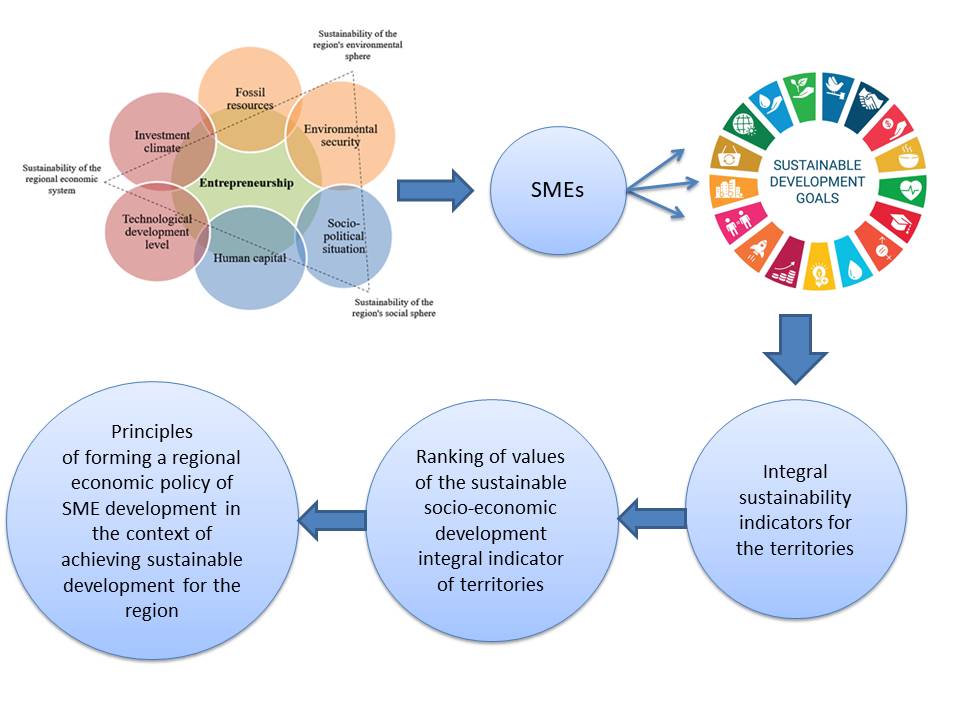
Sustainable development has become a prominent
reference point in strategic planning and territorial improvement. Economic
growth necessitates intensified efforts to utilize resources, often resulting
in increased pressure on the environment and heightened social inequality. The
application of sustainable development principles holds particular importance
for urbanized territories. Assessing the regional sustainability integral
indicator can help alleviate unequal socio-economic development among
municipalities. This indicator comprises indexes of the sustainability of
individual territories. The authors propose the integral indicator as the
arithmetic mean of indexes reflecting the sustainable development level of each
component (economic, social, environmental). The authors applied this tool to
municipalities in the Leningrad Region. Additionally, they conducted a ranking
of municipal districts in the region based on the integral indicator. The
leaders in sustainable development were the districts included in the St. Petersburg
agglomeration. The authors suggest that a significant factor in the sustainable
development of a territory is the presence of small enterprises, which possess
the necessary flexibility for innovation in the social and environmental
spheres. The authors propose distributing the elements of small and
medium-sized enterprises (SME) potential according to the sustainable
development factors of the region. The obtained data will enable the making of
administrative decisions at the municipal and regional levels, including those
related to the intensity and support for SMEs operating in relevant industries.
This methodological approach to assessing the sustainability of the region and
its internal municipalities, particularly concerning SMEs, can be utilized to
make optimal administrative decisions related to government support for
specific business areas.
Medium-sized enterprises (SME); Municipal territories; Region; Sustainability indicator; Sustainable development
The concept of sustainable economic development emerged in the mid-20th
century when various environmental and socio-economic challenges began to pose
threats to the well-being of both current and future generations (known as the
"sustainable development" concept). There is a note that issues
related to sustainable development (SD) have become relevant in the last few
decades. The idea of sustainable development corresponds to the global nature
of society's problems, and many states and their constituents use it to develop
effective
management strategies for socio-economic systems (Gutman
et al., 2022;
Sustainable
development has particular importance for highly urbanized areas, including
agglomerations. In general, we can say that even though there are some studies
on the relationship and contradictions between the goals of sustainable
development and urbanization (Zhang et al.,
2023; Chen et al., 2022; Griazev et al., 2021; Shkiperova and
Kurilo, 2021; Solovyova and Bogdanova, 2021; Li and Lu, 2021; Hák, Janoušková,
and Moldan 2016), there are no unified ideas about all the factors
affecting the sustainable development of territories.
Several
authors emphasize the improvement of public and municipal governance, including
digital technologies, as a necessary condition for the sustainable development
of territories (Halla, Merino-Saum, and Binder,
2022; Konstantinova et al., 2022; Tanina et al., 2022; Tanina et al.,
2021; Feleki, Vlachokostas, and Moussiopoulos, 2020; Zaborovskaya, Kudryavtseva,
and Zhogova, 2019). Other researchers emphasize transforming commercial
enterprises based on sustainable development principles (Evseev, Morozova, and Vasileva 2021). Yet some authors
highlight social and environmental entrepreneurship, which serves the
realization of public goals (Tanina et al.,
2023; Gregori, Holzmann, and Wdowiak 2021; Méndez-Picazo, Galindo-Martín, and Castaño-Martínez,
2021). However, the problem of assessing the impact of environmental and
social entrepreneurship development on the achievement of sustainable
development goals is still unresolved, although some studies have considered
individual enterprises in sustainability aspects (Diaz-Sarachaga
and Ariza-Montes, 2022; Grilo and Moreira, 2022; Kichigin et al., 2021; Chivu, 2019; Egorova et al.,
2019). To ensure sustainable
socio-economic development in countries, it is essential to focus on the
development of regions and territories (Kuznetsova,
2014).
The
authors suppose that small businesses are a significant factor in the
territory's sustainable development. A reason is that small businesses have the
optimal flexibility to innovate in the social and environmental spheres, but it
is necessary to provide public support to increase efficiency (Orel and Zaborovskaya, 2021; Pokrovskaya, Dolotova, and
Pavlova, 2021). Most authors believe sustainable socio-economic
development considers the unity of the economic, social, and environmental
spheres, so we claim the triad "economy - social sphere - ecology."
Thus, the article of Berawi (2023) describes
the ideas of balancing economic progress and environmental restoration for
social well-being.
The authors consider the
sustainability of the regional economic system as a constituent element of the
sustainability of socio-economic development.
Ensuring
the sustainability of the regional economic system implies, on the one hand,
giving priority attention to the conditions for economic activity in the
region. This approach aims to facilitate economic growth as a prominent source
of regional resources. On the other hand, this economic activity should
consider the needs of the social sphere and environmental protection while
achieving social and environmental objectives using market mechanisms and
principles. The authors (Orel and Zaborovskaya,
2021; Pokrovskaya, Dolotova, and Pavlova, 2021) propose to understand
the sustainable development of the regional economic system based on the triad
"economy - social sphere - ecology", in which the regional economy
development is considered based on a balance of economic, social, and
environmental objectives with reliance on the "green economy"
principles. It ensures economic growth and solves social and environmental
problems using adequate instruments.
Several
factors impact the sustainability of the regional economic system (Figure.1):
economic factors (investment climate and the innovative development level);
social factors (socio-political situation and human capital); and environmental
factors (fossil resources and environmental safety).
Entrepreneurial activity can be
an element that can provide complex interrelationships of these factors. At the
same time, it affects the aspects and is affected by them at the same time.
Investment climate and entrepreneurship are also inextricably linked. The
investment climate, as a set of economic, financial, and socio-political
conditions in a region, significantly impacts an investor's propensity to
invest and, consequently, an entrepreneur's propensity to do business in the
territory.
Figure 1 Entrepreneurship as a factor affecting each element
of the "economy - social sphere - ecology" triad
The
entrepreneur gains access to financial resources, more developed
infrastructure, and a larger market. In turn, a high level of private sector
development in the territory is a positive signal for the stakeholders to
decide on further investments. The technological development level and
entrepreneurship are also interrelated categories. Entrepreneurs actively
introduce innovations and modern technologies to optimize costs and increase
profits. In entrepreneurship, natural and fossil resources are used as the
basis for commercial production activities. The same basis could be relevant to
renewable resources. Some entrepreneurs use them to achieve a competitive
advantage within the green economy framework. Environmental safety within the
entrepreneurial activity framework is relevant to improving competitiveness and
increasing the attractiveness of commercial organizations to investors. At the
same time, the ecological security state-formed requirements restrict
entrepreneurship development.
The
socio-political situation influences the level of entrepreneurial risk
activity, the prospects for infrastructure development in business, and the
growth of specific branches of specialization. Simultaneously, the level of
entrepreneurship development and the nature of its activities can have an
impact on the socio-political landscape. Human capital is a pivotal factor in
shaping the entrepreneurial activity context. The human capital quality and
quantity development level depends on the business climate and the socio-economic
situation. The big business's role in achieving sustainable development goals
is recognized. There is a confirmation by the relevance of the ESG
(environmental, social, governance) agenda, which determines the corporate
policy of large, advanced companies in the social and environmental spheres, as
well as management, because of the high level of their financial capabilities.
At
the same time, there is an underestimation of the SME's potential to achieve
sustainability in the regional economic system. The 17 Sustainable
Development Goals (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in 2015 should serve as
guiding principles for the region's development.
The SME sector
influences the recruitment and stability of the middle class, which is
innovatively active. The efficiency growth of small enterprises contributes to
the increase of the region's economic potential. The choice of the
environmental and social spheres as the basis allows us to gain a synergetic
effect (table 1). Table 1 highlights the areas of influence of SMEs on the
sustainability of the region's socio-economic development. There are numbers of
the «Sustainable Development Goals» (SDGs) adopted by the United Nations in
parentheses.
Table
1
Elements of the SME sector's potential for regional development in terms of
sustainable development factors
|
Economic factor |
Social factor |
Ecological factor |
|
improving the financial well-being of the people (SDG inclusion and significant contribution to the
region's exports (SDG a significant contribution to the GDP region (SDG making a competitive environment in the region (SDG stable inflow of tax revenues to the budget (SDG |
middle-class formation, a layer of small owners in
the region, which leads to an increase of the social stability in the society
(SDG ensuring the new jobs (SDG reducing inequality of incomes and opportunities (SDG promotion of human potential development,
satisfaction need for self-realization (SDG prompt introduction of new innovative developments (SDG |
implementation of resource-saving technologies (SDG restoration of natural objects (SDG implementation of activities in service and
environmentally friendly industries (SDG |
At the same time, within the
"green economy" framework, the reference types of entrepreneurial
activity simultaneously solve economic, social, and environmental problems
using innovations.
Determining
the priorities of regional economic policy to support small and medium-sized
enterprises, the authors made a methodological approach to improving regional
monitoring based on a spatial map of the sustainability triad "economy -
social sphere - ecology" for municipalities of the region.
The authors
used such research methods in the study as analysis, synthesis, grouping,
generalization, and ranking. Using analysis and synthesis, the authors obtained
data on the current state of the studied objects.
The authors
chose the Leningrad region as the approbation object of the proposed methods.
Some reasons conditioned such choice. The
Leningrad region is a leading region in terms of socio-economic and innovation
development, often referred to as a donor region as it contributes more to the
federal budget than it receives from it. Accordingly, the Leningrad Region can
implement programs to aid small and medium-sized enterprises. These aid
programs have significant financial funding. Thus, the funds allocated in 2023
from the regional and federal budgets to aid SMEs in the Leningrad Region are 1
billion 230 million rubles (Government of the
Leningrad Region, 2023). However, this region does not have a concept or
strategy for sustainable development, and there is a high level of
differentiation in the development of municipalities. Therefore, it is
necessary to improve the distribution of financial funds for SME aid,
considering the need to achieve sustainable development and the differences
between municipalities in the region.
The grouping
and generalization methods could identify and group the primary elements of the
Leningrad Region's sustainable development and define the specifics of the
municipalities' development. The ranking allowed us to obtain a rating of
municipal territories in the region according to the sustainability indexes
proposed by the authors.
Methodological principles of building an integral indicator of
sustainable socio-economic development of the region are considering the UN
sustainable development goals, information base availability, simplicity of
calculations, possibilities of indicators transformation, and considering the
interrelations in the triad "economy - ecology - social sphere."
The authors selected indexes based on statistical data on the development
of municipalities and on the ability of these indexes to characterize the
sustainability of development (sustainable development goals of
municipalities). Also, the authors selected the indexes for all municipalities
in the region. Official statistics on municipalities have a limited set of indices,
resulting in a constrained range of variables available for the methodology
implementation.
The authors also chose the indicators that determine the economic
sustainability of the Leningrad Region inner districts: the volume of shipped
industrial products in 2022 per capita, in thousand rubles; the investment
volume in fixed capital by businesses- total in 2022 per capita, in thousand
rubles; retail trade turnover - total in 2022 per capita, in thousand rubles;
the balanced financial result of organizations to the number of SME, in million
rubles; the number of SME per 1000 people.
The authors used these indicators to calculate social sustainability:
average monthly nominal gross salary, in rubles; the average number of
employees; registered people in the Employment Center with the status of
"Unemployed" and "Looking for work" in 2022 to the
population, %; birth rate (per 1000 people) in 2022; death rate (per 1000
people) in 2022.
Also, the authors chose such indicators determining environmental
sustainability as the area percentage occupied by forestries, forest parks, and
urban forests, %; bathing places (percent of official areas to the number of
generic bathing places), %; gross emissions of carbon monoxide (CO) from motor
vehicles in large cities of Leningrad Region municipalities, emission ton/year;
content of phenol pollutant components in soils of impacted monitoring sites
with background values, mg/kg; emissions of pollutants from stationary sources
per inhabitant by municipal districts and urban district, kg.
Based on the indicators, it is possible to obtain sustainability
indicators for municipalities and the region. There is a proposition to apply
the comparative analysis method based on the Euclidean distance approach. It
allows us to identify the indicator ideal and then assess the
proximity-distance degree of other regions' indicators relative to the ideal
value. For this purpose, the authors express indexes of the territories in
fractions relative to the ideal index, defined as one (see equation 1):
ai, bi – level of development of the i-th region
according to the indicator;
xi – the indicator
value;
max xi, min xi
– the ideal index value, which authors accept as the limit value of indexes.
The authors determine the levels of economic, social, and environmental
sustainability by the arithmetic mean (see equation 2):
Uj – the sustainability
level indicator of each component of sustainable, balanced development (Uj
accepts value Uecon, Usoc,
Uecol )
Ki- value of individual indexes
of economic, social, and environmental sustainability.
n- number of individual indexes of economic, social, and environmental
sustainability.
At the final stage, the authors form an integral indicator as the
arithmetic mean of sustainable development level indicators of each component
(economic, social, environmental). Based on this, the integral indicator of
sustainable socio-economic development of the region is (see equation 3):
Uecon –economic sustainability
Usoc – social
sustainability
Uecol – ecological
sustainability
The integral indicator should be within the range from 0 to 1. An example
of ranking the indicator values according to the "traffic light"
principle is in Table 2. The ranking is established on the values of the
integral index U. The choice of limit values is based on the need to identify
three zones characterizing the degree of sustainability of the municipality's
development. It is sufficient at this study stage. As empirical data
accumulates in dynamics, the researchers may refine the scale. The approach to
scaling is based on the article of Kuznetsova M.N. (Kuznetsova,
2015).
Table 2 Ranking of values of the
sustainable socio-economic development integral indicator of territories
|
Limit values |
Sustainable development interpretation |
Territory identification zone |
|
0 to 0.1 |
Unsustainable
development |
Red zone |
|
0.1 to 0.4 |
Weakly sustainable development | |
|
0.4 to 0.7 |
Medium sustainable development |
Yellow zone |
|
0.7 to 0.9 |
Sustainable development |
Green zone |
|
0.9 to 1 |
Highly sustainable development |
Constructing an integral
sustainability indicator methodology for municipal territories allows us to
obtain a rating of municipalities in the Leningrad Region by the sustainability
and balanced development degree (Figure. 2). According to the adopted ranking,
medium sustainable development is characteristic of most municipalities of the
Leningrad Region - 12 districts are in the yellow zone. The leaders among the
municipal districts of the Region are the Kingiseppsky, Lomonosovsky, and
Vsevolozhsky districts. Kingiseppsky District has high economic development per
capita due to the significant contribution of the Ust-Luga commercial sea port.
The authors note that all of the leading territories in terms of sustainability
are part of the St. Petersburg agglomeration. Kirovsky, Volkhovsky,
Slantsevsky, Lodeynopolsky, Tikhvinsky, and Podporozhsky municipal districts
have weak sustainable development. These districts are in the red zone.
For sustainable development territory formation, it is
necessary to improve the regional economic policy. The authors view the
regional economic policy supporting Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in the
pursuit of long-term sustainable development within the region as an
interconnected set of methods, mechanisms, and instruments of influence on economic
entities in the SME sector. This policy is designed to foster economic growth
and social development while taking into account environmental constraints.
This
regional economic policy type would be an appropriate strategy that combines
the planned projects and programs within the sustainable development framework
into a coherent system, which makes it possible to choose the most promising
and effective strategic support directions from the "green economy"
perspective" (Table 3).
Figure 2 Rating of
sustainability of Leningrad Region municipalities and urban areas
There
are some offers on implementation tools of regional economic policy. The first
is a new approach to the SME classification in the environmental and social
sphere to differentiate the economic support. The second tool is a methodology
for assessing the sustainability development of municipalities in the region
using the proposed indicators and the "traffic light" map. The third
tool is an algorithm for provision monitoring of financial support to SMEs
according to the sustainability triad.
Table 3 Principles of forming a regional economic
policy of SME development in the context of achieving sustainable development
for the region
|
Principle |
Principle essence | |
|
1. Program approach and measurability of goals
in the public support implementation |
Public support consolidation for SMEs in
sectors that contribute to achieving sustainable development of the region.
Attracting investments in "green" innovations. Setting key
performance indicators for public support programs, measurability of goals
based on SMART-analysis | |
|
2. Availability of public support at all stages
of innovation implementation for SME |
Public support promotion by stages (active
investment in marketing research, research and development, testing, design,
technological and organizational production preparation, and commercial
implementation of innovations). | |
|
3. Innovation infrastructure
advanced development |
Effective interaction of executive and
legislative authorities, business, and scientific institutions, the purpose
of which is the innovation infrastructure development to ensure a
"green" transition at small and medium-sized enterprises. The stakeholders
must introduce and develop the "single window" principle for
business support. | |
|
4. Public support transparency for business |
Free and clear access (using the "single
window" system) will ensure information transparency on the amount, recipients,
and characteristics of specific programs (projects) that obtained public
support. | |
|
5. Identification of activity priority areas |
It is a regulatory consolidation of innovative,
social, and environmental business goals. | |
|
Principle |
Principle essence | |
|
6. Priority use of market instruments and
public-private partnership instruments to stimulate priority business sectors
|
It is a business infrastructure support for
businesses' development that contributes to the sustainable development achievement
in the region. There are investments in research and development, promoting
them in the markets of "green" innovations with subsequent
commercialization. Also, this principle is about scientific and technical
initiatives stimulation for young scientists and students of higher education
institutions, attracting young people to priority areas. | |
|
7. Ensuring the public support effectiveness
for innovation activities for socio-economic development goals and federal
subjects of the Russian Federation |
Introduction of transparent qualitative and
quantitative target indicators of the work effectiveness of specialized
committees, infrastructure organizations' support, and enterprises receiving
support. Monitoring of the SME turnover share by receiving support from
enterprises operating in the innovation, social, and environmental sectors. | |
There is a
proposition to monitor the SMEs in the region throughout the year. Also, there
is a proposal to assign the monitoring and financial support functions to the
executive authorities to the Committee for Support of Small and Medium Business
and Consumer Market and the Committee for Economic Development of the Leningrad
Region, as well as to the SME support infrastructure organizations - the
Entrepreneurship Support Fund of the Leningrad Region and municipal SME support
funds. According to the authors, the question of the degree of influence of
individual factors on the sustainable development of municipal territories is
debatable. A significant error in assessing such an impact may be caused by the
lack of reliable and up-to-date statistical information.
This study uses available municipal statistics, which
determined the limited list of indexes, as well as the relative simplicity of
the methodology. This article (Gutman et al., 2022) studies an impact assessment of business
activities on the region's sustainable development. However, the list of
indexes utilized in this article poses challenges for application at the
municipal level due to a lack of available data. For example, there is data on
life expectancy in the region and no data for municipalities. Also, the article
authors (Gutman et al., 2022) focus
on the impact of large businesses on the regional economy and choose regions
with large enterprises for analysis, while the authors of this study
concentrate on the impact of small and medium-sized businesses which are
dispersed across the territory of the region and municipalities, which makes
the methodology applicable to most regions.
The article (Khaykin and
Toechkina, 2021) analyzes service capital as a condition for the
sustainable development of society with an emphasis on the social sphere. At
the same time, the authors do not provide a quantitative approach to assessing
the level of such capital about sustainability; moreover, the environmental
component is not considered part of service capital, which makes it problematic
to apply the approach to assess the sustainability of municipalities in the
region. The article (Berawi, 2021) describes the intersectoral interaction that helps to
achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals. The aid of small and medium-sized
businesses, whose activities are related to solving social and environmental
problems of the region, regarding the severity of these problems at the
municipal level (which can be assessed based on the proposed methodology),
contributes to increasing the effectiveness of intersectoral interaction.
The proposed methodology uses Kuznetsova's methodology
adaptation and development (Kuznetsova, 2014).
In the article of M.N. Kuznetsova, "the method of comparative analysis,
which uses the method of Euclidean distances, is applied. It allows us to
identify the ideal index and assess the degree of proximity distance of indexes
of other regions relative to the ideal value".
The "ideal" value of the index is determined by the
achieved value by the municipalities of the region (i.e., the "best"
municipality is selected from those studied by this index). This approach is
the ideal system concept (the concept proposition was in the theory of
inventive problem solving). The ideal system does not exist but sets some
values of indexes, which ideally should be strived for to determine the vector
of management actions. The adaptation and development of the approach (Kuznetsova, 2014) consists of selecting new
objects (municipalities), justifying the set of indexes for calculating
individual indexes for the municipal level, and supplementing the ranking scale
with the "traffic light" principle.
The proposed methodology is applicable to analyze
sustainability in other regions. However, it is necessary to understand that
there are similar data on the development of municipal entities in another
region. If data are contrasting, the methodology can be adapted to a new group
of indexes. The prospect of further research may be the improvement of
methodology for calculating the integral indicator. The weights of each
component in the considered approach are assumed to be equal since obtaining
estimates of the development balance of municipal entities is a necessary
sustainability component. In the future, as data accumulates, the weighted
average formula will also be applicable. Accordingly, the task will be to
substantiate and determine the weighting coefficients.
The
research problem revolves around selecting indexes to characterize the
sustainability of municipal development. These indexes should be universally
available to facilitate the assessment of all municipalities, involving
statistical observation across these indexes for comprehensive evaluation.
Unfortunately, the list of indexes of official statistics that satisfy these
requirements is currently not broad. One of the research development ways can
be the justification and development of the list of indexes of municipal
statistics in the sustainability context, which will help to improve regional
monitoring. The proposed method applies to the system of regional monitoring.
Prospects for further research are related to the specific algorithm
development for monitoring implementation.
Directions for further research include
studying the economic and political systems of foreign countries with a high
sustainable development index, as well as further identifying the dependence of
the level of development of social and eco-oriented entrepreneurship on
achieving sustainable development in the region.
It is advisable to study the experience
of other countries in achieving sustainable development goals for studying
sustainable development strategies, mechanisms, and tools for their implementation,
including from the point of view of the impact on SMEs whose activities
contribute to the sustainability of socio-economic development (primarily
environmental and social entrepreneurship). In this context, it is necessary to
identify the leading countries in achieving the UN Sustainable Development
Goals, analyze the availability and content of sustainable development
strategies in foreign countries, including a comparison of these positions with
the leading countries, review the SME aid system in the top countries and
identify the most effective aid tools with a focus on environmental and social
entrepreneurship.
Also, a future research area is the
study and generalization of approaches presented in the experience of other
countries to environmental and social entrepreneurship identification as an
object for priority state aid. This article considers the methodology of
obtaining an integral assessment of the sustainability of a municipality and
private assessments of economic, environmental, and social sustainability.
Based on these assessments, the authors underline "problem" areas for
the territory and an opportunity to provide additional state aid to those SMEs
that operate in the relevant field (based on the environmental and social entrepreneurship
identification) to solve the problems.
The article discusses the assessment of municipal
sustainability in the Leningrad Region, Russia, with a focus on sustainable
development principles. The authors propose an integral indicator for
sustainability that considers economic, social, and environmental factors. The
authors emphasize the importance of SMEs in achieving sustainable development
and suggest distributing SME potential based on sustainability factors. To assess sustainability,
the authors select various components related to economic, social, and
environmental aspects. The authors propose an integral indicator that combines
these components and ranks municipalities of the Leningrad Region based on
their sustainability levels. The results show that most municipalities in the
Leningrad Region exhibit medium sustainable development, with some districts
being stronger in economic sustainability due to factors like commercial
seaports. The authors highlight the need for improved regional economic
policies to support SMEs in achieving sustainable development. Also, the authors suggest
principles for forming regional economic policies, including a program
approach, public support at all stages of innovation, innovation infrastructure
development, transparency, and priority areas, such as social and environmental
fields. In conclusion, the article presents a methodological approach to assess
regional sustainability and SME potential, offering insights for making
informed administrative decisions related to government support for specific
business areas.
The
research was financed as part of the project "Development of a methodology
for instrumental base formation for analysis and modeling of the spatial
socio-economic development of systems based on internal reserves in the context
of digitalization" (FSEG-2023-0008).
Berawi, M.A., 2021.
Managing Cross-Sectoral Coordination in Accelerating the Sustainable
Development Agenda. International Journal of Technology, Volume 12(2),
pp. 228–231
Berawi, M.A., 2023. Smart
Cities: Accelerating Sustainable Development Agenda. International Journal
of Technology, Volume 14(1), pp. 1–4
Brazovskaia, V., Gutman,
S., 2021. Classification of Regions by Climatic Characteristics for the Use of
Renewable Energy Sources. International Journal of Technology, Volume
12(7), pp. 1537–1545
Chen, M., Chen, L., Cheng,
J., Yu, J., 2022. Identifying Interlinkages Between Urbanization and
Sustainable Development Goals. Geography and Sustainability, Volume
3(4), pp. 339-346
Chivu, L., 2019. Local Entrepreneurship
and Social Services in Romania. Territorial Analysis. European Research on
Management and Business Economics, Volume 25(2), pp. 79–86
Diaz-Sarachaga, J.M.,
Ariza-Montes, A., 2022. The Role of Social Entrepreneurship in the Attainment
of the Sustainable Development Goals. Journal of Business Research,
Volume 152, pp. 242–250
Egorova, S., Bogdanovich,
I., Kistaeva N., Kulachinskaya, A., 2019. Environmental costs as an indicator
of sustainable development. In: Proceedings of the International
Scientific Conference on Energy, Environmental and Construction Engineering
(EECE-2019) E3S Web Conferences, Volume 140, p.7
Evseev, A., Morozova, N.,
Vasileva, I., 2021. Digital Activity of Industrial Enterprises in the Context
of Ensuring Sustainable Economic Development of Territories. In:
Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific Conference on
Innovations in Digital Economy (SPBPU IDE '20). Association for Computing
Machinery, New York, USA, Article 30, pp. 1–5
Feleki, E., Vlachokostas,
C., Moussiopoulos, N., 2020. Holistic Methodological Framework for the Characterization
of Urban Sustainability and Strategic Planning. Journal of Cleaner
Production, Volume 243, p. 118432
Government of the
Leningrad Region, 2023. Current Theme: NATIONAL PROJECTS: There are More Small Businesses
in the Leningrad Region. Available online at:
https://lenobl.ru/ru/dlya-smi/news/59603, Accessed on December 1, 2023
Gregori, P., Holzmann, P.,
Wdowiak, M.A., 2021. For the Sake of Nature: Identity Work and Meaningful Experiences
in Environmental Entrepreneurship. Journal of Business Research, Volume
122, pp. 488–501
Griazev, M., Sabinina, A.,
Sycheva, I., Izmalkova, S., Sycheva, N., 2021. Actualization of Environmental
Education as an Innovative and Digital Resource for Sustainable Regional
Development. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International
Scientific Conference on Innovations in Digital Economy (SPBPU IDE '20).
Association for Computing Machinery, New York, USA, Article 11, pp. 1–7
Grilo, R., Moreira, A.C.,
2022. The Social as the Heart of Social Innovation and Social Entrepreneurship:
Anemerging Area or an Old Crossroads? International Journal of Innovation
Studies, Volume 6 (2), pp. 53–66
Gutman, S., Rytova, E.,
Brazovskaia, V., Skhvediani, A., 2022. The Impact of Firms’ Activities on
Regional Sustainable Development. International Journal of Technology,
Volume 13(7), pp. 1505–1514
Hák, T., Janoušková, S.,
Moldan, B., 2016. Sustainable Development Goals: A need for Relevant Indicators.
Ecological Indicators, Volume 60, pp. 565–573
Halla, P., Merino-Saum,
A., Binder, C.R., 2022. How to Link Sustainability Assessments with Local Governance?
– Connecting Indicators to Institutions and Controversies. Environmental
Impact Assessment Review, Volume 93, P. 106741
Khaykin, M., Toechkina,
O., 2021. Service Capital as a Condition for the Sustainable Development of
Society. International Journal of Technology, Volume 12(7), pp. 1458–1467
Kichigin, O., Zaytsev, A.,
Gorskiy, V., Bogacheva, T., 2021. Analysis of Russian and World Experience in
Solving Problems of Waste Management at the Regional Level. In:
Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific Conference on
Innovations in Digital Economy (SPBPU IDE '20). Association for Computing
Machinery, New York, USA, Article 55, pp. 1–6
Konstantinova, Y., Kuksin,
I., Styf, M., Shukhov, F., 2022. Eco-activism and the State: the Situation in
Russia in the Digital Age. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International
Scientific Conference on Innovations in Digital Economy (SPBPU IDE '21).
Association for Computing Machinery, New York, USA, pp. 348–355
Kuznetsova, M.N., 2015.
Assessment of the Quality of Human Capital of Regions in the Russian Federation.
Economics and Entrepreneurship, Volume 7(60), pp. 339–345
Kuznetsova, M.N., 2014.
Ensuring Sustainable Balanced Development of the Region Based on Improving the Quality
of Human Capital: Specialty 08.00.05 "Economics and Management of the National
Economy: dissertation for the academic degree of Candidate of Economic Sciences.
Gatchina, Volume 181
Li, X., Lu, Z., 2021.
Quantitative Measurement on Urbanization Development Level in Urban
Agglomerations: A case of JJJ Urban Agglomeration. Ecological Indicators,
Volume 133, p. 108375
Méndez-Picazo, M.-T.,
Galindo-Martín, M.-A., Castaño-Martínez, M.-S., 2021. Effects of Sociocultural
and Economic Factors on Social Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Development. Journal
of Innovation and Knowledge, Volume 6 (2), pp. 69–77
Orel, A.A., Zaborovskaya,
O.V., 2021. Improving mechanisms of entrepreneurship support in Leningrad
region as foundation for sustainable development. Journal of Legal and Economic Research,
Volume 1. pp. 136–143
Pokrovskaya, L., Dolotova,
N., Pavlova, E., 2021. Evaluating the Effectiveness of Implementing Targeted
Programs for Small Businesses in a Megalopolis. In: Proceedings of the 2nd
International Scientific Conference on Innovations in Digital Economy (SPBPU
IDE '20). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, USA, Article 62, pp.
1–6
Shkiperova, G.T., Kurilo,
A.E., 2021. Assessment of The Sustainability of Regional Socio-Ecological-Economic
Systems. Market Economy Problems, Volume 1, pp. 47–61
Solovyova, E., Bogdanova,
T., 2021. Research Into The Level of Sustainable Development in The Middle
East. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Scientific
Conference on Innovations in Digital Economy (SPBPU IDE '20). Association for
Computing Machinery, New York, USA, Article 41, pp. 1–7
Tanina, A., Konyshev, E.,
Abidova, D., Kryzhko, D., 2021. Strategic Approaches to the Management of
Tourism Sustainable Development: The Russian and German Experience. In:
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Tourism Research,
ICTR 2021, pp. 520–29
Tanina, A., Konyshev, E.,
Veprikova, A., Smetanina, A., 2022. Features of the use of Digital Technologies
by Tourists During COVID-19 (on the Example of the Kirov Region). In:
Proceedings of the 3rd International Scientific Conference on
Innovations in Digital Economy (SPBPU IDE '21). Association for Computing
Machinery, New York, USA, pp. 262–269
Tanina, A.V., Tashenova,
L.V., Mamrayeva, D.G., Konyshev, E.V., 2023. State Support Measures for the
Tourism Industry During the Covid-19 Pandemic: Digital Solutions. In: International
Scientific Conference “Digital Transformation on Manufacturing, Infrastructure
& Service" Cham: Springer Nature Switzerland, pp. 66–86
Zaborovskaya, O.,
Kudryavtseva, T., Zhogova, E., 2019. Examination of Mechanisms of Regional Sustainable
Development Strategy as Exemplified by the Leningrad Region, International
Journal of Engineering and Advanced Technology, Volume 9 (1), pp. 5065–5076
Zhang, Y., Zhu, T., Guo, H., Yang, X., 2023. Analysis of the Coupling
Coordination Degree of the Society-Economy-Resource-Environment System in Urban
Areas: Case Study of the Jingjinjiurban Agglomeration, China. Ecological
Indicators, Volume 146, p. 109851
