The Role of Leader and the Effect of Customer’s Smart Factory Investment on Firm’s Industry 4.0 Technology Adoption in Thailand
Corresponding email: chawalit@siit.tu.ac.th
Published at : 20 Jan 2022
Volume : IJtech
Vol 13, No 1 (2022)
DOI : https://doi.org/10.14716/ijtech.v13i1.4814
Chumnumporn, K., Jeenanunta, C., Simpan, S., Srivat, K., Sanprasert, V., 2022. The Role of Leader and the Effect of Customer’s Smart Factory Investment on Firm’s Industry 4.0 Technology Adoption in Thailand. International Journal of Technology. Volume 13(1), pp. 26-37
| Kwanchanok Chumnumporn | School of Management Technology, Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University, 99 Moo 18, Khlong Luang, Pathum Thani 12120, Thailand |
| Chawalit Jeenanunta | School of Management Technology, Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University, 99 Moo 18, Khlong Luang, Pathum Thani 12120, Thailand |
| Suchinthara Simpan | School of Management Technology, Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University, 99 Moo 18, Khlong Luang, Pathum Thani 12120, Thailand |
| Kornkanok Srivat | School of Management Technology, Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University, 99 Moo 18, Khlong Luang, Pathum Thani 12120, Thailand |
| Vararat Sanprasert | School of Management Technology, Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University, 99 Moo 18, Khlong Luang, Pathum Thani 12120, Thailand |
Manufacturers
are aware of Industry 4.0 trends due to the new technologies and the
transformation of processes that require new competencies of employees and an
integrated system in the supply chain network. The purpose of this paper is to
examine the role of a leader through a transformational leadership style and
the effect of a customer’s smart factory investment on a firm’s Industry 4.0
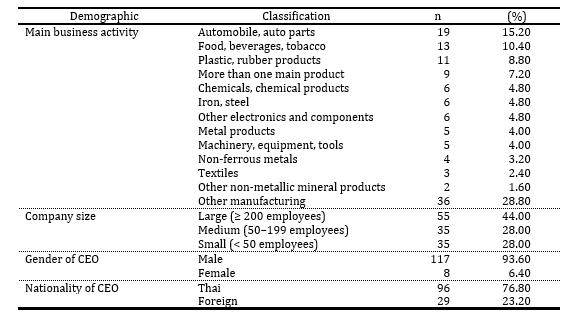
technology adoption in the Thai manufacturing industry. In total, 125 valid
samples from different companies surveyed in the Thai manufacturing industry were
used to analyze the mentioned relations. The multiple regression results show
that a leader’s transformational leadership and external pressure, such as a customer’s
smart factory investment, have positive impacts on a firm’s operational
technology (OT) and information technology (IT) adoptions. These results reveal
that successful technology implementation requires both internal and external
factors to push for organizational change.
Effect of customer’s smart factory investment; Industry 4.0; Technology adoption; Transformational leadership;
Industry 4.0 or the smart factory is an industrial revolution that challenges manufacturing companies. Operational technology (OT) and information technology (IT) are converging by using the Internet of Things (IoT), cyber-physical systems (CPS), big data, and analytical, artificially intelligence, cloud computing, and autonomous robots (Schumacher et al., 2016; Fatorachian and Kazemi, 2018; Berawi, 2020). These advanced technologies are transforming products, processes, and business models to form new industrial patterns. The development results of the fourth industrial revolution are not only the new technologies but also a new entrepreneurial mindset (Sterev, 2017). For this reason, business leaders play an essential role in developing and motivating their individual followers by determining and setting clear missions and visions (Wang and Howell, 2012; Cinnio?lu, 2020). Top management strategies pose significant challenges to managing employees to change their behaviors and adopt new technologies (Ihua, 2009). Various research studies on the modern leadership theory have explored the distinct attributes of a leader who has a transformational leadership style as an agent of change (Yu et al., 2002; Hallinger, 2003; Bass and Riggio, 2006). Thus, it is essential to study how transformational leadership affects Industry 4.0 technology adoption.
While large-sized companies are very flexible in their investments to upgrade their technologies toward Industry 4.0, small- and medium-sized companies (SMEs) have limited budgets, knowledge, and expertise. These barriers faced by SMEs bring a low level of Industry 4.0 technology implementation in their enterprises. Nguyen’s (2009) study about the impacts of internal and external forces on IT adoption shows that customer pressure positively affects the IT adoption of manufacturers, especially SMEs. Similarly, Intalar and Jeenanunta’s (2019) research has confirmed the positive influence of a customer’s information and communication technology (ICT) investment on a supplier’s ICT adoption. Thus, this study includes the effect of a customer’s smart factory investment as another empirical factor.
The key research question addressed in this study includes an analysis testing of the impact of transformational leadership and the effect of a customer’s smart factory investment on a firm’s OT/IT adoption. The rest of this paper is organized as follows: The theoretical background and the hypotheses are presented in Section 2. The hypothesis model is empirically tested in Section 3, and the results are discussed in Section 4. Finally, the conclusions are drawn in Section 5.
The
main purpose of this paper is to investigate how transformational leadership
(internal factor) and the effect of a customer’s smart factory investment
(external factor) affect a firm’s OT and IT adoption. Successful technology
adoption requires leaders to play an important role in designing the core
technological values, purpose, and vision by creating policies, strategies, and
structures that will guide their organizations toward successful technology
integration and implementation. Additionally, there is strong evidence that
when customers invest in new technologies related to Industry 4.0, this will
affect their suppliers’ Industry 4.0 technology adoption. The same level of
technology aims to reduce coordination failures between manufacturers and their
suppliers. Therefore, the top management executives (CEOs) should have a vision
toward Industry 4.0 or a smart factory to lead their firms to achieve digital
transformation. Moreover, the firms need to establish strong relationships and
collaboration with their customers to learn how to improve their OT/IT systems
and create automation in the production process. The higher level of automation
in manufacturing processes aims to reduce the manufacturing lead time, increase
productivity, and enhance product quality.
This study has not examined other
internal and external dimensions. Further research could link other leadership
theories (such as those involving leadership skills, leadership behavior, and agile
leadership etc.) with a firm’s technology adoption to analyze the former’s
influence on the latter. Researchers could also include other external factors,
such as the government’s Industry 4.0 policy, which supports manufacturers in
collaborating with an external organization (e.g., a government labor training
institution and a university) to upgrade a technology and upskill/reskill
employees. It is also important to determine the appropriate strategic to
enhance the success of Industry 4.0 technology in each business size in
Thailand. Thus, further studies should test the initial hypothesis to
investigate the effects of the leadership style and customer investment on a
firm’s technology adoption in the different contexts of the business size, the leader’s
gender, and the leader’s nation. Furthermore, this study has conducted a narrow
analysis. Future research should apply a non-linear regression method to
investigate the effects of transformational leadership and a customer’s smart
factory investment on a firm’s Industry 4.0 technology adoption.
This
research was fully supported by the Center of Excellence in Logistics and
Supply Chain Systems Engineering and Technology (COE LogEn), Sirindhorn
International Institute of Technology, Thammasat University.
Alam, S.S., Noor, M.K.M., 2009. ICT Adoption in Small and
Medium Enterprises: An Empirical Evidence of Service Sectors in Malaysia. International
Journal of Business and Management, Volume 4(2), pp. 112–125
Bass, B.M., 1999. Two Decades of Research and
Development in Transformational Leadership. European Journal of Work and
Organizational Psychology, Volume 8(1), pp. 9–32
Bass, B., Riggio, R., 2006. Transformational
Leadership (2nd ed.). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc., Mahwah, New Jersey, USA
Bencsik,
A., 2020. Challenges of Management in the Digital Economy. International
Journal of Technology, Volume 11(6), pp. 1275–1285
Berawi, M.A., 2020. Managing Artificial Intelligence
Technology for Added Value. International Journal of Technology, Volume 11(1), pp. 1–4
Cinnio?lu, H., 2020. A Review
of Modern Leadership Styles in Perspective of Industry 4.0. In: Agile
Business Leadership Methods for Industry 4.0, Emerald Publishing Ltd., pp. 1–23
Cirgref, 2019. IT/OT Convergence: A Fruitful
Integration of Information Systems and Operational Systems. Available
Online at
https://www.cigref.fr/cigref-report-it-ot-convergence-a-fruitful-integration-of-information-systems-and-operational-systems,
Accessed on January 6, 2021
Consoli, D., 2012. Literature Analysis on Determinant
Factors and the Impact of ICT in SMEs. Procedia - Social and Behavioral
Sciences, Volume 62, pp. 93–97
Davuto?lu, N.A., 2018. Sanayi 4.0’?n Liderlik Ve Insan
Kaynaklar? Yönetimine Alg?sal Etkileri. Journal of Social and Humanities
Sciences Research (JSHSR), Volume 5(30), pp. 4041–4048
Eisenbach, R., Watson, K., Pillai, R., 1999.
Transformational Leadership in the Context of Organizational Change. Journal
of Organizational Change Management, Volume 12(2), pp. 80–88
Fabiani, S., Schivardi, F., Trento, S., 2005. ICT
Adoption in Italian Manufacturing: Firm-Level Evidence. Industrial and
Corporate Change, Volume 14(2), pp. 225–249
Fatorachian, H., Kazemi, H., 2018. A Critical
Investigation of Industry 4.0 in Manufacturing: Theoretical Operationalisation
Framework. Production Planning & Control, Volume 29(8), pp. 633–644
Frank, A.G., Dalenogare, L.S., Ayala, N.F., 2019.
Industry 4.0 Technologies: Implementation Patterns in Manufacturing Companies. International
Journal of Production Economics, Volume 210, pp. 15–26
Gardner, W.L., Avolio, B.J., 1998. The Charismatic
Relationship: A Dramaturgical Perspective. Academy of Management Review,
Volume 23(1), pp. 32–58
Golovina, T., Polyanin, A.,
Adamenko, A., Khegay, E., Schepinin, V., 2020. Digital Twins as a New Paradigm
of an Industrial Enterprise. International Journal of Technology, Volume 11(6), pp. 1115–1124
Gumusluoglu, L., Ilsev,
A., 2009. Transformational Leadership,
Creativity, and Organizational Innovation. Journal of Business
Research, Volume 62(4), pp. 461–473
Haider, A., 2012. Information and Operational
Technologies Governance Framework for Engineering Asset Management. In:
Mathew, J., Ma, L., Tan, A., Weijnen, M., Lee, J. (Eds.), Engineering Asset
Management and Infrastructure Sustainability, Springer, London
Hair, J.F., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., Anderson, R.E.,
2019. Multivariate Data Analysis (8th ed.). Cengage Learning, EMEA,
Hampshire, UK
Hallinger, P., 2003. Leading Educational Change:
Reflections on the Practice of Instructional and Transformational Leadership. Cambridge
Journal of Education, Volume 33(3), pp. 329–351
Howell, J.M., Avolio, B.J., 1993. Transformational
Leadership, Transactional Leadership, Locus of Control, and Support for
Innovation: Key Predictors of Consolidated-Business-Unit Performance. Journal
of Applied Psychology, Volume 78(6), pp. 891–902
Hwang, C., Yan, W., Scherer, R.F., 1996. Understanding
Managerial Behaviour in Different Cultures: A Review of Instrument Translation
Methodology. International Journal of Management, Volume 13(3), pp.
332–339
Ihua, U.B., 2009. SMEs Key Failure-Factors: A
Comparison Between the United Kingdom and Nigeria. Journal of Social
Sciences, Volume 18(3), pp. 199–207
Ikram, W., Thornhill, N.F., 2010. Wireless
Communication in Process Automation: A Survey of Opportunities, Requirements,
Concerns and Challenges. In: UKACC International Conference on Control
2010, pp. 1–6
Illa, P.K., Padhi, N., 2018. Practical Guide to Smart
Factory Transition using IoT, Big Data and Edge Analytics. IEEE Access,
Volume 6, pp. 55162–55170
Intalar, N., Jeenanunta, C., 2019. Effects of
Customer’s Investment in ICT on Partners’ Decisions Through the Supply Chain:
An Empirical Study of the Manufacturing Industry in Thailand. Asian Journal
of Technology Innovation, Volume 27(2), pp. 239–256
Jafari, S.M., Osman, M.R., Yusuff, R.M., Tang, S.H.,
2006. ERP Implementation in Malaysia: The Importance of Critical Success
Factors. International Journal of Engineering and Technology, Volume
3(1), pp. 125–131
Koçel, T., 2014. ??letme Yöneticili?i (Business
Management). ?stanbul, Beta Bas?m
Koerber, B., Freund, H., Kasah, T., Bolz, L., 2018.
Leveraging Industrial Software Stack Advancement for Digital Transformation. Digital
McKinsey, (August), pp. 1–50
Lee, J., Bagheri, B., Kao, H.A., 2015. A Cyber-Physical
Systems Architecture for Industry 4.0-Based Manufacturing Systems.
Manufacturing Letters, Volume 3, pp. 18–23
Lowe, K.B., Kroeck, K.G., Sivasubramaniam, N., 1996.
Effectiveness Correlates of Transactional and Transformational Leadership: A
Meta-Analytic Review of the MLQ Literature. Leadership Quarterly, Volume
7(3), pp. 385–425
Matsumoto, D., 1994. People: Psychology from A
Cultural Perspective, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company. Pacific Grove, CA
Mumford, M.D., Zaccaro, S.J., Harding, F.D., Jacobs,
T.O., Fleishman, E.A. 2000. Leadership Skills for a Changing World: Solving
Complex Social Problems. Leadership Quarterly, Volume 11(1), pp. 11–35
Nguyen, T.U.H., 2009. Information Technology Adoption
in SMEs: An Integrated Framework. International Journal of Entrepreneurial
Behavior and Research, Volume 15(2), pp. 162–186
Northouse, P.G., 2016. Leadership: Theory and
Practice (7th
ed.). Sage Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA
Sako, M., 2004. Supplier Development at Honda, Nissan
and Toyota: Comparative Case Studies of Organizational Capability Enhancement. Industrial
and Corporate Change, Volume 13(2), pp. 281–308
Schepers, J., Wetzels, M., de Ruyter, K., 2005.
Leadership Styles in Technology Acceptance: Do Followers Practice What Leaders
Preach? Managing Service Quality, Volume 15(6), pp. 496–508
Schumacher, A., Erol, S., Sihn, W., 2016. A Maturity
Model for Assessing Industry 4.0 Readiness and Maturity of Manufacturing
Enterprises. Procedia CIRP, Volume 52(1), pp. 161–166
Seyal, A.H., 2015. Examining the Role of
Transformational Leadership in Technology Adoption: Evidence from Bruneian
Technical and Vocational Establishments (TVE). Journal of Education and
Practice, Volume 6(8), pp. 32–43
Sterev, N., 2017. Marketing Leadership: The Industry
4.0 Need of Next Generation Marketing. Trakia Journal of Science, Volume
15(1), pp. 99–103
The, Y., Kuusk, A.G., 2021. Aligning IIoT and ISA-95
to Improve Asset Management in Process Industries. In: Crespo Márquez
A., Komljenovic D., Amadi-Echendu J. (Eds) 14th WCEAM Proceedings,
WCEAM 2019, Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering, Springer, Cham
Van de Vliert, E., 2006. Autocratic Leadership Around
the Globe; Do Climate and Wealth Drive Leadership Culture? Journal of
Cross-Cultural Psychology, Volume 37(1), pp. 42-59
Vanichbuncha, K., 2012. Statistic for Research.
Chulalongkorn University Bookshop, Bangkok
Wang, X.H.F., Howell, J.M., 2012. A Multilevel Study
of Transformational Leadership, Identification, and Follower Outcomes. The
Leadership Quarterly, Volume 23(5), pp. 775–790
Waziri, A.Y., Ali, K.N., Aliagha, G.U., 2015. The
Influence of Transformational Leadership Style on ICT Adoption in the Nigerian
Construction Industry. Asian Social Science, Volume 11(18), pp. 123–133
Youssef, A.B., Merino, D.C., Hadhri, W., 2012. Determinants
of Intra-Firm Diffusion Process of ICT: Theoretical Sources and Empirical Evidence
from Catalan Firms. In: Allegrezza, S., Dubrocard, A. (Eds.), Internet
Econometrics, Palgrave Macmillan, London, pp. 288–312
Yu, H., Leithwood, K., Jantzi, D., 2002. The Effects
of Transformational Leadership on Teachers’ Commitment to Change in Hong Kong. Journal
of Educational Administration, Volume 40(4), pp. 368–389
Yukl, G., 1999. An Evaluation of Conceptual
Weaknesses in Transformational and Charismatic Leadership Theories. Leadership
Quarterly, Volume 10(2), pp. 285–305
